Terrestrial Energy and the Production of Carbon-Free Ammonia
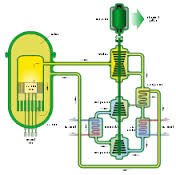
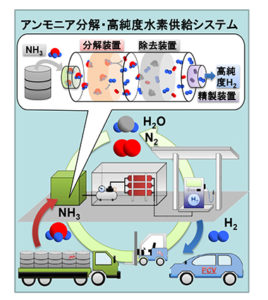
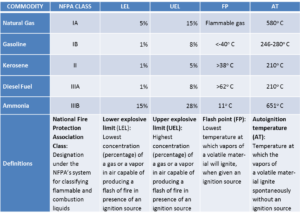
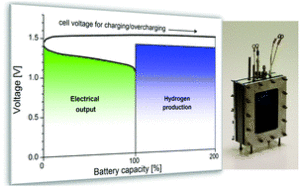
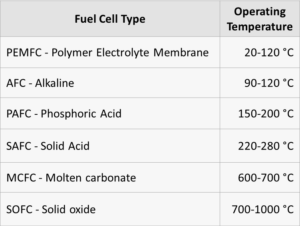
On January 24, the nuclear energy company Terrestrial Energy USA informed the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission of its plans “to license a small modular, advanced nuclear reactor in the United States.” Many steps later – sometime in the 2020s – the American subsidiary of the Canadian company Terrestrial Energy, Inc., hopes to bring its IMSR technology to market. IMSR stands for integral molten salt reactor. The IMSR stands apart from conventional nuclear technology on several dimensions. On the dimension of operating temperature, the IMSR is hot enough that it can be beneficially integrated with high-temperature industrial processes. According to the company’s research, ammonia production could be a candidate for such integration.