Content Related to Australian National University
Global emissions implications from co-combusting ammonia in coal fired power stations: An analysis of the Japan-Australia supply chain
Producing cheap, clean hydrogen: new updates
Three new updates this week:
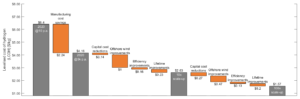
1. A team at Durham University has shown that a massive scale-up of PEM electrolyser manufacturing capability can slash the capital costs of producing electrolyser units by up to 70%.
2. A team from the University of Campinas has proposed more focus on electrolysis of waste and seawater to produce hydrogen, avoiding direct competition between drinking water and hydrogen production.
3. A team from the Australian National University has demonstrated a new pathway forward for hydrogen production directly from sunlight by demonstrating a stable, efficient photocatalyst.
Ammonia trade and embedded emissions pricing
AEA Australia Announces 2020 Conference
Pandemic or no pandemic, the Australian chapter of the Ammonia Energy Association (AEA Australia) will hold a second edition of its Ammonia = Hydrogen 2.0 Conference this year. The event will be held on a virtual basis on August 27 and 28 from 1:00 to 5:00 p.m. (Australian Eastern Standard Time) each day. The conference tagline is “Building an energy export industry using Green Ammonia.” Its themes this year will be “green ammonia production — jobs for the regions;” “ammonia as maritime bunker fuel;” and “ammonia certification schemes.” The opening address, entitled “Ammonia — is it a fuel, or is it an energy carrier?” will be given by Alan Finkel, Chief Scientist of the Australian Government.
International R&D on sustainable ammonia synthesis technologies
Over the last few weeks, I've written extensively about sustainable ammonia synthesis projects funded by the US Department of Energy (DOE). While these projects are important, the US has no monopoly on technology development. Indeed, given the current uncertainty regarding energy policy under the Trump administration, the US may be at risk of stepping away from its assumed role as an industry leader in this area. This article introduces seven international projects, representing research coming out of eight countries spread across four continents. These projects span the breadth of next-generation ammonia synthesis research, from nanotechnology and electrocatalysis to plasmas and ionic liquids.
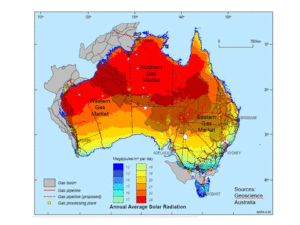
Australia's Concentrated Solar Fuels Program
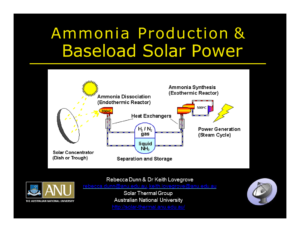
Solar ammonia' could be the key to the sustainable energy economies of two nations. During his talk at the 2016 NH3 Fuel Conference, Keith Lovegrove, Head of Solar Thermal at IT Power Group in Australia, said that Japan and Australia have the opportunity to move their trade in energy onto a climate-friendly foundation. This would involve development of Australia's solar resources in a way that helps Japan ramp up its Strategy for Hydrogen & Fuel Cells in the coming decades.
Ammonia Production and Baseload Solar Power