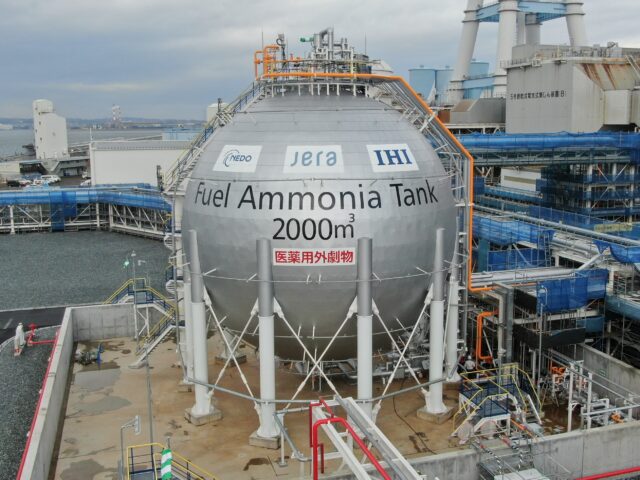
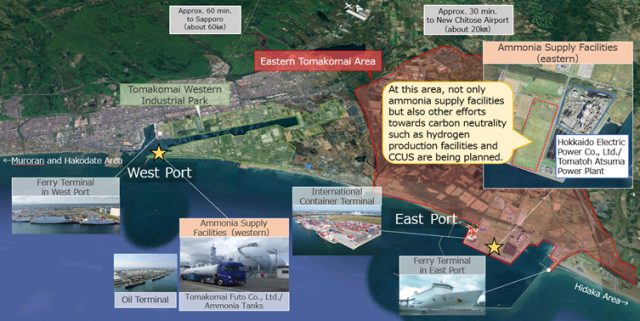
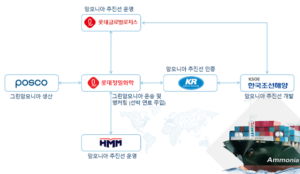
Multiple ammonia import bases are under development in Asia. In Singapore, Vopak and Air Liquide will explore new infrastructure on Jurong Island. In South Korea, Ulsan Port Authority and NGO Pacific Environment will cooperate to accelerate the transition of Ulsan into an “eco-friendly” port. And in Japan, IHI will lead two study consortia exploring new supply and distribution hubs in Hokkaido and Fukushima.
Content Related to IHI Corporation
Establishing ammonia import bases in Singapore, South Korea and Japan
JERA begins ammonia co-firing demonstration at Hekinan
With installation and testing of ammonia fuel equipment now complete, a 20% ammonia co-firing demonstration will proceed from April to June this year at the Hekinan power plant. JERA and IHI aim for commercial operations to begin around March 2025. JERA is also exploring part ownership and offtake from Exxon Mobil’s CCS ammonia mega-project in Baytown, Texas.
GE, IHI progress ammonia gas turbine technology roadmap
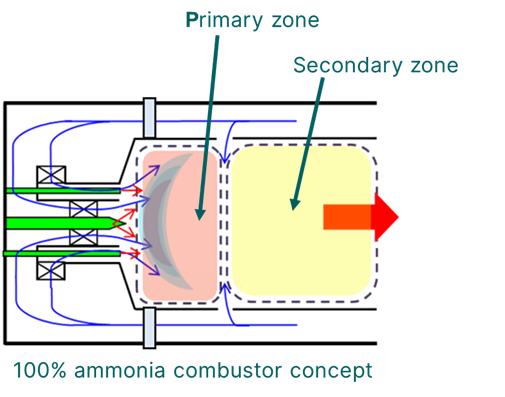
GE Vernova and IHI Corporation will proceed to the engineering and testing phase for their ammonia gas turbine roadmap for Asia. Based on their efforts in 2022 to demonstrate a low-N2O combustor for a 2 MW, 100% ammonia-fired turbine, IHI will lead development of a two-stage combustor for larger-scale gas turbine models.
ACME to supply renewable ammonia to IHI in Japan
ACME and IHI have signed an offtake agreement for the supply of renewable ammonia from the pair’s under-development production plant in Odisha, eastern India. On a long-term basis, 400,000 tons per year will be transported, with production to begin in 2027. A number of other Indian production projects were launched this month.
New terminal infrastructure for ammonia energy imports: Japan, Netherlands & Africa
IHI & Vopak will explore the development and operation of large-scale ammonia terminals in Japan, focused on the cost-effective distribution of ammonia imports. In the Netherlands, Proton Ventures reports that work on the conversion of Vesta Terminal’s existing site into an ammonia import hub is on schedule for FID to be made by 2024. And in other Proton Ventures news, the organisation has been awarded a FEED contract with Geldof to develop an ammonia terminal in Western Africa.
Discussions on standardization of clean fuel ammonia
Exploring ammonia retrofits at the Sakra power plant, Singapore
Sembcorp, IHI and GE will explore potential retrofits to existing gas turbines at the Sakra power plant to run on 100% ammonia fuel. The Sakra plant currently features two GE 9FA turbines, which are among the models IHI & GE are targeting for development of a “retrofittable” ammonia combustion system.
IHI joins Australian renewable ammonia consortium
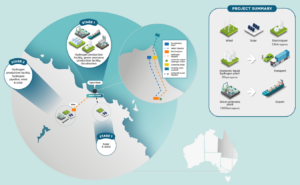
IHI Corporation will join the North Queensland Clean Energy Project, a consortium developing a GW-scale electrolysis, ammonia production and export facility in north Queensland, Australia. Project partners include Idemitsu Australia, CS Energy and Energy Estate.
Japan consortium to explore ammonia imports to Osaka
Mitsui & Co., Mitsui Chemicals, IHI Corporation and the Kansai Electric Power Company will explore the establishment of a hydrogen & ammonia supply chain based in Osaka. Ammonia fuel will be used to decarbonise electricity generation, and cracked to provide a feedstock for other industrial processes like steel-making. In South Korea, a similar partnership is evolving between LOTTE and Air Liquide. You can learn more about the emerging nexus between ammonia cracking and steel-making at our upcoming annual conference in Atlanta, USA.
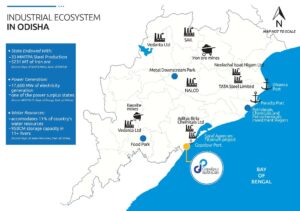
ACME & IHI: new ammonia mega-project in Odisha
The pair will jointly develop a 1.3 million tonnes per year renewable ammonia production plant in the Gopalpur Industrial Park in Odisha, northeast India. From the adjacent port, ammonia will be shipped domestically, and exported to key global markets.
Creating Ammonia Value Chain for the Smooth Transition toward Carbon Neutrality
ACME Group, IHI to join forces on ammonia
ACME and IHI will assess the feasibility of potential joint projects in the ammonia energy space, including production, transportation, distribution, and power generation. Also this week, IHI and GE have presented their findings from an ammonia-powered gas turbine feasibility study, with some favorable fuel economics for ammonia.
Trailing ammonia-coal co-firing in India
Adani Power and two Japanese organisations - IHI Corporation and Kowa - have signed a new MoU to conduct a feasibility study into 20% ammonia-coal co-firing at the Mundra power plant in Gujarat, India. The trio will also investigate increasing this co-firing percentage all the way up to 100% ammonia fuel (“mono-firing”). The new MoU contributes to a national-level partnership announced last week - the "India-Japan Clean Energy Partnership (CEP)".
JERA targets 50% ammonia-coal co-firing by 2030
Japanese government funding via NEDO will support four critical ammonia energy projects, including JERA's new plan to demonstrate 50% ammonia-coal co-firing by 2030. Other projects include improved catalysts for ammonia production, low-temperature and low-pressure synthesis pathways, and developing 100% ammonia-fed boilers and gas turbines. In addition, a new cooperation agreement between ASEAN countries will see Japan support other members to adopt their ammonia energy solutions, particularly coal co-firing.
Woodside outlines scale for green ammonia project in Tasmania
Woodside Energy secured land this week for its H2TAS project in Bell Bay, Tasmania. A long-term lease on a partially-cleared project site nearby the Bell Bay Advanced Manufacturing Zone will be home to up to 1.7 GW of electrolysers, and a target production of 200,000 tonnes per year green ammonia. Last month Woodside also announced the H2Perth project: a world-scale, 1,500 tonnes per day hydrogen production facility aimed at local markets for refueling fuel cell vehicles, and international markets via export in the form of liquefied hydrogen or ammonia.
Mitsubishi Power developing ammonia combustion boilers
Mitsubishi Power has announced the development of single and mixed-fuel ammonia combustion boilers for industrial applications. Importantly, Mitsubishi also announced that optimal combustion conditions for ammonia have been successfully identified to minimise NOx formation and ammonia slip.
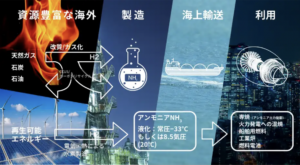
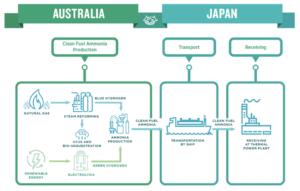
Exploring an ammonia fuel supply chain between Australia and Japan
Woodside Energy, JOGMEC, Marubeni and two Japanese power utilities signed a joint research agreement this week to investigate the feasibility of a blue ammonia supply chain between Australia and Japan.
The Ammonia Wrap: 45 GW mega-project in Kazakhstan and more
This week: 45 GW mega-project in Kazakhstan, world-first industrial "dynamic" green ammonia plant, Japan's Idemitsu to use Tokuyama facility for ammonia imports, co-combustion test, more successful funding rounds, green ammonia in Ireland, South Africa's potential to fuel green shipping: new report, Obsky LNG becomes Obsky hydrogen/ammonia and more developments in the Middle East.
The Ammonia Wrap: a roadmap for ammonia-fueled gas turbines in Asia and more
This week: a roadmap for ammonia-fueled gas turbines in Asia, ammonia solutions in Iceland, IMO sets new decarbonisation milestone, new ammonia-powered vessels planned, maritime study developments, Australian updates (Fortescue, AREH and Itochu in Gladstone), Fertiglobe joins Abu Dhabi blue ammonia project and Statkraft's Porsgrunn plans.
The Ammonia Wrap: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE and more
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE, RWE, BASF combine for 2 GW "Offshore-to-X" project, green ammonia exports from Tasmania, coal co-combustion trials in Japan, Japanese shipping industry chases decarbonisation, South Korean companies join together in local green ammonia consortium, new funding for ammonia-from-wastewater research and Horisont Energi and Equinor join forces for the Polaris project.
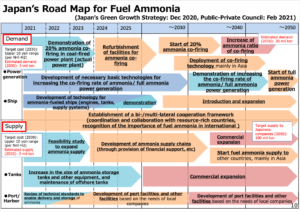
Japan's Road Map for Fuel Ammonia
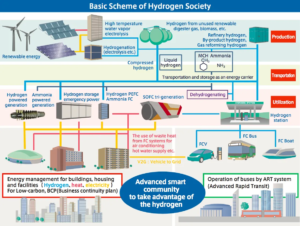
This month, the Japanese Ministry for Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) began promoting an updated Road Map for Fuel Ammonia, focused on the use of ammonia in thermal power plants and as a shipping fuel. By 2030, Japan expects to import 3 million tons of clean ammonia, with demand rising to 30 million tons by 2050. To secure these volumes, Japanese companies are now making investments up and down the supply chain. These are ambitious numbers, matching Japan’s recent commitment to reach net-zero emissions, but still they miss the big picture. The broader economic opportunity arrives when Japanese companies export their fuel ammonia technologies, decarbonizing coal-fired power plants across Asia, and then supply the fuel to these newly sustainable shipping and electricity sectors. By 2050, the METI Road Map expects Japanese trading companies to supply the wider region with 100 million tons per year of clean ammonia.
METI Forms Ammonia Energy Council
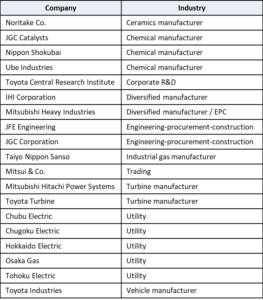
Last week, Japan’s Ministry of Energy, Trade, and Industry (METI) announced the formation of a council to work on the implementation of ammonia as an energy commodity. The announcement came on the same day as a speech by Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga in which he established 2050 as the date certain for Japan to achieve carbon-neutrality. That was Monday October 26, 2020. The council held its first meeting on Tuesday October 27. The Council consists of four entities from the public sector and ten from the private sector. Members include companies that have previously been identified with the development of ammonia energy systems, including EPC firm JGC, capital goods manufacturer IHI, electric utility JERA, and shipping company NYK Line. The membership also reflects what appears to be the group’s central mission: positioning Japan as ammonia energy’s global leader via the dissemination of technology and the development of supply chains.
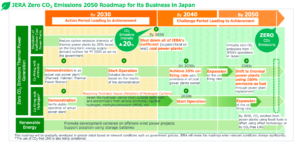
Japan's Electricity Sector: An Early Market for Low-Carbon Ammonia
This week, Japan’s new Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga announced that by 2050 the country would drive its greenhouse gas emissions to zero and achieve carbon-neutrality. Earlier in the month, the Japanese electric utility JERA announced its intention of “achieving zero CO2 emissions by 2050.” Its first step toward this goal was its 'JERA Zero CO2 Emissions 2050 Roadmap for its Business in Japan.'
A Deep Dive into SIP “Energy Carriers” Ammonia Combustion Research (second half)
From 2014 to 2018 Bunro Shiozawa served as Deputy Program Director of the SIP “Energy Carriers” initiative in Japan. Over the last year he has published a ten-part series of articles that describe and reflect on the research supported by the initiative. Part 4 covers ammonia combustion technologies. The first half of the article was posted on September 23, 2020, in Shiozawa's English translation. The second half follows.
Japan's NYK and partners to develop ammonia fueled and fueling vessels
In recent weeks, the Japanese shipping company NYK Line has announced a series of high-profile research and development collaborations that aim to establish ammonia fueled vessels and fuel supply. Its partners in these projects include classification society Class NK, engine manufacturer IHI Power Systems, and shipbuilder Japan Marine United Corporation. Three vessel types have been announced, so far, including an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier, an ammonia barge for offshore bunkering, and an ammonia-fueled tugboat (for navigating the barge). Pushing beyond the initial research phase, these collaborations aim for commercialization and to put these vessels “into practical use.”
Industry consortium announces feasibility study for co-firing ammonia in thermal power plants
In March 2020, IHI Corporation, JERA Co., and Marubeni Corporation announced a feasibility study "to evaluate possible applications for the co-firing of ammonia in thermal power plants." The Japanese companies have contracted with NEDO to deliver detailed technical and economic analysis on the use of ammonia as a direct fuel for power generation. In addition, with support from Woodside Energy in Australia, they "will examine the construction and operation of world-scale ammonia facilities and the optimisation of supply chain costs" to support "large-scale export of hydrogen as ammonia."
Japan Advances SOFCs for the Built Environment
A steady stream of Japanese news reports over the last several months attest to the country’s progress in deploying fuel cells in the built environment. Dubbed “Ene-Farms,” the appliances function as micro-scale combined heat and power units, providing electricity as well as heat for domestic applications. Most of the Ene-Farms deployed so far feature proton-exchange membrane (PEM) technology (which requires high-purity hydrogen). However, two recent developments show that solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) technology (well suited for ammonia) could play a role, maybe even a large role, in Japan's Hydrogen Society.
Green Ammonia Consortium: A Force for Ammonia Energy
Japan’s Green Ammonia Consortium, an industry body dedicated to building “a value chain from supply to use of CO2-free ammonia,” launched its Web site on December 5. The site features plenty of interesting content, but most significant may be the roster of members. Eighty seven companies, public organizations, and individuals are listed. Taken together they represent a significant force for ammonia energy implementation in Japan and beyond.
New Technology of the Ammonia Co-Firing with Pulverized Coal to Reduce the NOx Emission
Performance of Ammonia/Natural Gas Co-Fired Gas Turbine with Two-Stage Combustor
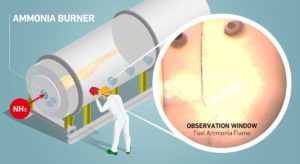
IHI Corporation pushes its ammonia combustion technologies closer to commercialization
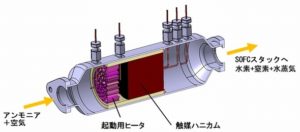
This week, an article in Japan Chemical Daily disclosed IHI Corporation's future plans for its range of ammonia combustion technologies, each of which has been demonstrated in the last year. These include "ammonia-coal co-fired thermal power boilers, ammonia-fired gas turbines and direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs)." Under the headline "IHI Speeds up Development of Several Ammonia-Based Technologies," the article describes the company's ambitions for scaling-up each of these technologies, and provides a schedule for its next set of demonstration projects.
IHI Breaks Ground on Hydrogen Research Facility
Japanese capital goods manufacturer IHI Corporation announced last month that it has started construction of a 1,000 square-meter hydrogen research facility in Fukushima Prefecture. The facility will be an addition to IHI’s Green Energy Center in Soma City which was launched in 2018. One of the Center’s original focuses is the production steps of the green hydrogen supply chain using solar electricity to power developmental electrolyzers. The new facility will focus on hydrogen carriers, including ammonia and methane (via “methanation” of carbon dioxide), that can be used in the logistics steps of the supply chain.
New Video Summarizes SIP Energy Carriers Accomplishments
ANNOUNCEMENT: The Japanese Government’s Cabinet Office and the Japan Science and Technology Agency have released an English-language video that summarizes the accomplishments of the Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program’s Energy Carriers initiative. The release coincides with the end-of-March conclusion of Energy Carriers’ work, and anticipates this month’s formal activation of the Green Ammonia Consortium.
Ammonia Gas Turbines on European R&D List
ETN Global’s latest R&D Recommendation was released in October 2018. ETN stands for European Turbine Network and its technology of interest is the gas turbine. The 2018 Recommendation is notable because it is the first that includes ammonia on the R&D agenda.
Technologies to use carbon free ammonia in power plant
Performance of Ammonia-Natural Gas Co-Fired Gas Turbine for Power Generation
Development of Catalytic Reactors and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Systems for Utilization of Ammonia
Ammonia for Fuel Cells: AFC, SOFC, and PEM
In the last 12 months ... IHI Corporation tested its 1 kW ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) in Japan; Project Alkammonia concluded its work on cracked-ammonia-fed alkaline fuel cells (AFC) in the EU; the University of Delaware's project for low-temperature direct ammonia fuel cells (DAFC) continues with funding from the US Department of Energy's ARPA-E; and, in Israel, GenCell launched its commercial 4 kW ammonia-fed AFC with field demonstrations at up to 800 locations across Kenya.
Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells Take Another Step Forward in Japan
Japanese manufacturing concern IHI reported on May 16 that it had “successfully generated 1 kW class power” from a direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cell. This is the latest milestone for a technology that could play a major role in the roll-out of Japan’s Hydrogen Society.
IHI First to Reach 20% Ammonia-Coal Co-Firing Milestone
The Japanese manufacturer IHI Corporation announced on March 28 that it had successfully demonstrated the co-firing of ammonia and coal in a fuel mix composed of 20% ammonia. Ammonia-coal co-firing had previously been demonstrated by Chugoku Electric in a fuel mix composed of just 0.6-0.8% ammonia. IHI says its ultimate goal is to “construct a value chain that connects the production and use of ammonia, using combustion technology of gas turbines and coal-fired boilers, using ammonia as fuel.”
IHI Commits to Ammonia Energy. Big Time.
During his presentation at the November 2017 NH3 Energy + Topical Conference, Shogo Onishi of IHI Corporation described the progress made by IHI and Tohoku University in limiting NOx emissions from ammonia-fired gas turbines (AGTs). Regular attendees of the annual NH3 Fuel Conference identify IHI with its work on AGTs since the company also addressed this topic at the 2016 and 2015 events. However, a scan of published materials shows that AGTs are just one aspect of IHI’s activity in the ammonia energy arena. In fact, IHI is also looking at the near-term commercialization of technologies in ammonia-coal co-firing in steam boilers and direct ammonia fuel cells. This level and breadth of commitment to ammonia energy is unique among global capital goods producers.
Green Ammonia Consortium Comes to the Fore in Japan
On December 8, the Nikkei Sangyo Shimbun ran a story about the future of coal-fired electricity generation in Japan. The story touched on topics ranging from the plumbing in a Chugoku Electric generating station to the Trump administration’s idiosyncratic approach to environmental diplomacy. And it contained this sentence: “Ammonia can become a ‘savior’ of coal-fired power.” Clearly an explanation is in order.
Methods for Low NOx Combustion in Ammonia / Natural Gas Dual Fuel Gas Turbine Combustor
Development of Materials and Systems for Ammonia-Fueled Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
SIP "Energy Carriers" video: ammonia turbines, industrial furnaces, fuel cells
To demonstrate the progress of the SIP "Energy Carriers" program, the Japan Science and Technology Agency last week released a video, embedded below, that shows three of its ammonia fuel research and development projects in operation. R&D is often an abstract idea: this video shows what it looks like to generate power from ammonia. As it turns out, fuel cells aren't hugely photogenic. Nonetheless, if a picture is worth a thousand words, this will be a long article.
Advances in Ammonia-Fired Gas Turbines Open Up Major Use Case
In the last 12 months ... Researchers seeking to fire gas turbines with ammonia made significant strides toward realization of commercial-scale machines in both the U.K. and Japan. This means that electricity generation has become a realistic near-term use-case for ammonia energy.
Green Ammonia Consortium: Bright Prospects in Japan for Ammonia as an Energy Carrier
In the last 12 months ... In July 2017, 19 companies and three research institutions came together to form the Green Ammonia Consortium. Before this development, it was unclear whether ammonia would find a significant role in Japan’s hydrogen economy. In the wake of this announcement, however, ammonia seems to have claimed the leading position in the race among potential energy carriers.
Major Development for Ammonia Energy in Japan
On July 25, the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) announced that a collection of companies and research institutions had come together to form a Green Ammonia Consortium. The 22-member group will take over responsibility for the ammonia aspect of the Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Program (SIP) Energy Carriers agenda when the SIP is discontinued at the end of fiscal 2018. A JST press release states that the Consortium intends to develop a strategy for “forming [an] ammonia value chain,” promote demonstration projects that can further commercialization, and enable “Japanese industry to lead the world market.”
Ammonia-Fueled Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Advance at Kyoto University
Earlier this month the Eguchi Laboratory at Kyoto University announced advances in ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cell technology. The lab was able to produce a functioning fuel cell with a power output of one kilowatt. The device attained “direct current power generation efficiency” in excess of 50% and reached 1,000 hours of continuous operation.
Industrial demonstrations of ammonia fuel in Japan
Most of the ammonia energy projects I write about are in the research and development phase but, as I've said before, technology transfer from the academic lab to commercial deployment is moving swiftly - especially in Japan. Last week, Nikkei Asian Review published two articles outlining plans by major engineering and power firms to build utility-scale demonstrations using ammonia as a fuel for electricity generation. Both projects aim to reduce the carbon intensity of the Japanese electrical grid, incrementally but significantly, by displacing a portion of the fossil fuels with ammonia. The first project will generate power using an ammonia-coal mix, while the second will combine ammonia with natural gas.
How to create a market for low-carbon ammonia: product labeling
I wrote last week about ARPA-E's "transformative" ammonia synthesis technologies, describing three technology pathways under development: low pressure Haber-Bosch, electrochemical processes, and advanced electrolysis. ARPA-E's ambitious R&D program might imply that a meaningful, commercial market for sustainable ammonia is still decades away. It represents, however, only the slow American tip of a fast-moving global iceberg. In Japan, where there's no debate about climate science, the national effort is already well underway, with three programs to develop low-carbon ammonia synthesis under the Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), 'Energy Carriers.'
Ammonia Turbine Power Generation with Reduced NOx
A common concern with ammonia fuel is that NOx emissions will be too high to control. However, in new research from Turkey, USA, and Japan, presented at this year's NH3 Fuel Conference in September 2016, two things became clear. First, NOx emissions can be reduced to less than 10ppm by employing good engineering design and exploiting the chemical properties of ammonia, which plays a dual role as both the fuel and the emissions-cleanup agent. Second, the deployment of ammonia-fueled turbines for power generation is not only feasible, but actively being developed, with demonstration units running today and improved demonstration projects currently in development.
Development of ammonia / natural gas dual fuel gas turbine combustor
Combustion characteristics of ammonia/natural gas dual fuel burner for gas turbine combustor