Chugoku Electric Power Company announced today that they have filed a patent application for a clean-power technology that involves co-firing ammonia with coal. The novel approach is attracting widespread interest.
Content Related to Japan Science and Technology Agency
Article
Chugoku Electric Completes Successful Trial, Seeks Patent for Ammonia Co-Firing Technology
Ammonia Energy News
September 28, 2017
Article
Japanese Cabinet Office Holds Energy Carriers Symposium
Stephen H. Crolius
August 24, 2017
Ammonia energy received favorable notice at the Energy Carriers "Open Symposium" held on July 26 by the Cabinet Office of the Japan Government. Hydrogen energy carriers are a key focus of Japan's Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program. The event took place at Hitotsubashi University in Tokyo. An observer estimated that approximately 400 attendees were present.
Presentation
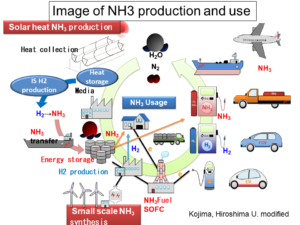
Ammonia as an Energy Carrier for Renewable Energy
At present, ammonia is mostly formed through reforming of natural gas (CH4). A 1,000 ton per day plant is said to consume about 35 GJ of natural gas to produce 1 ton of ammonia (22.5 GJ of enthalpy). About 50% of extra energy is wasted. If 1 ton ammonia is produced through water electrolysis, 22.5 GJ of electricity is necessary theoretically. Here again, extra electric energy must be wasted. The author discusses roughly how the efficiency depends upon the process size and the renewable energy cost.