Content Related to Stanford University
Technoeconomic Requirements for Sustainable Ammonia Production
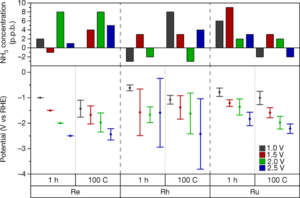
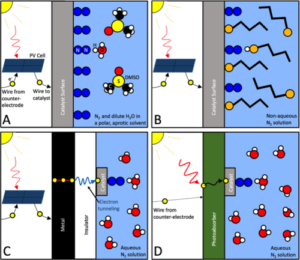
A rigorous protocol for measuring electrochemical ammonia synthesis rates
NEWS BRIEF: A paper published this week in Nature addresses the challenge of accurately reporting synthesis rates for electrochemical ammonia production technologies. According to the authors, from Stanford University, the Technical University of Denmark (DTU), and Imperial College London, it is not always clear if new technologies really synthesize ammonia, or if the researchers simply measured contaminants. This is because, at experimental scale, materially significant amounts of ammonia (or other nitrogen-containing molecules) could be present in the air, membranes, catalysts, or simply the researchers' breath. To support the development of viable electrochemical ammonia synthesis technologies, the authors propose "benchmarking protocols," and "a standardized set of control experiments."
Stanford Convenes Hydrogen Focus Group
ANNOUNCEMENT: California's Stanford University held a two-day workshop this week to launch a new effort aimed at advancing hydrogen “for stable, long-term, low-carbon energy storage.” The Stanford Hydrogen Focus Group intends to support research, serve as a technical resource, and disseminate information via workshops and symposia.
Overcoming the Selectivity Challenge in Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis
In the last 12 months ... The research community has made great progress toward solving the "selectivity challenge" in electrochemical ammonia synthesis. Although, rather than an actual solution, mostly what we have is a range of sophisticated work-arounds that succeed in making this problem moot.
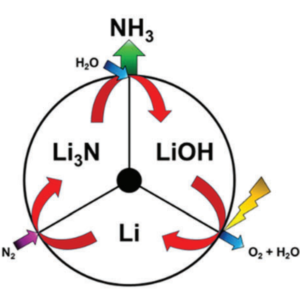
Sustainable ammonia synthesis: SUNCAT's lithium-cycling strategy
New research coming out of Stanford University suggests a fascinating new direction for electrochemical ammonia synthesis technology development. The US-Danish team of scientists at SUNCAT, tasked with finding new catalysts for electrochemical ammonia production, saw that 'selectivity' posed a tremendous challenge - in other words, most of the energy used by renewable ammonia production systems went into making hydrogen instead of making ammonia. The new SUNCAT solution does not overcome this selectivity challenge. It doesn't even try. Instead, these researchers have avoided the problem completely.
US DOE funding research into sustainable ammonia synthesis
The US Department of Energy (DOE) is currently supporting six fundamental research projects that will develop "novel catalysts and mechanisms for nitrogen activation," which it hopes will lead to future sustainable ammonia synthesis technologies. These projects, announced in August 2016 and administered by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, aim "to investigate some of the outstanding scientific questions in the synthesis of ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) using processes that do not generate greenhouse gases."