Content Related to West Virginia University
Microwave Catalytic Synthesis of Ammonia for Energy Storage and Transformation
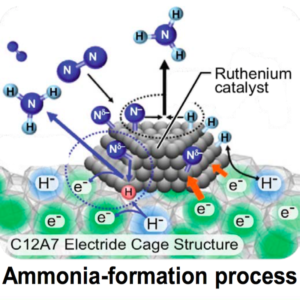
Microwave Catalysis for Ammonia Synthesis Under Mild Reaction Conditions
Future Ammonia Technologies: Electrochemical (part 3)
This series of articles on the future of ammonia synthesis began with a report on the NH3 Energy+ conference presentation by Grigorii Soloveichik, Program Director at the US Department of Energy's ARPA-E, who categorized the technologies as being either improvements on Haber-Bosch or electrochemical (with exceptions). ARPA-E invests in "transformational, high-risk, early-stage research," and recently began funding ammonia synthesis technologies, not to make renewable fertilizer but to produce "energy-dense zero-carbon liquid fuel." This article will introduce the six electrochemical technologies currently in development with funding from ARPA-E.
Future Ammonia Technologies: Plasma, Membrane, Redox
I wrote recently about two pathways for ammonia production technology development: improvements on Haber-Bosch, or electrochemical synthesis. Last week, I covered some of these Haber-Bosch improvements; next week, I'll write about electrochemical processes. This week, I want to write about some innovations that don't fit this two-way categorization: they don't use electrochemistry and they don't build upon the Haber-Bosch process, and that might be the only thing that links them.
ARPA-E funding for renewable ammonia synthesis technologies
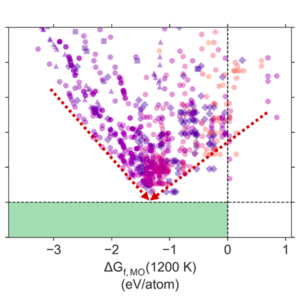
Last week, ARPA-E announced funding for eight technologies that aim to make ammonia from renewable electricity, air, and water. The technological pathways being developed include adaptations of the Haber-Bosch process - seeking improvements in catalysts and absorbents - as well as novel electrochemical processes.
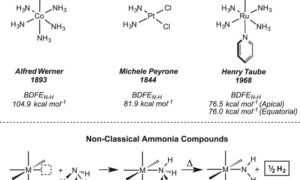
Coordinated scission of N-H bonds
A paper published in this week's edition of Science outlines a new approach to breaking the hydrogen-nitrogen bonds in ammonia, allowing the production of hydrogen at low temperatures. This research was also reported on phys.org under the headline: "Method found for pulling hydrogen from ammonia for use as clean fuel."
Your Carbon or Your Life: Ammonia vs. Emissions