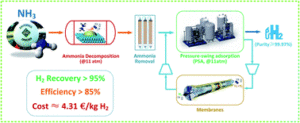
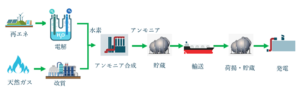
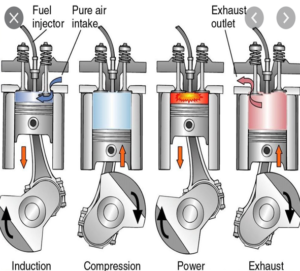
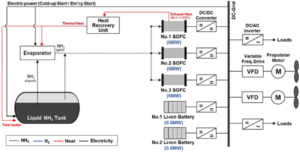
At least four major maritime ammonia projects have been announced in the last few weeks, each of which aims to demonstrate an ammonia-fueled vessel operating at sea.
In Norway, Color Fantasy, the world's largest RORO cruise liner, will pilot ammonia fuel. Across the broader Nordic region, the Global Maritime Forum has launched NoGAPS, a major consortium that aims to deploy "the world's first ammonia powered deep sea vessel" by 2025.
In Japan, a new industry consortium has launched that goes beyond on-board ship technology to include "owning and operating the ships, supplying ammonia fuel and developing ammonia supply facilities." And the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), which published its roadmap last month, aims to demonstrate ammonia fuel on "an actual ship from 2028" — specifically, a 80,000 dwt ammonia-fueled bulk carrier.