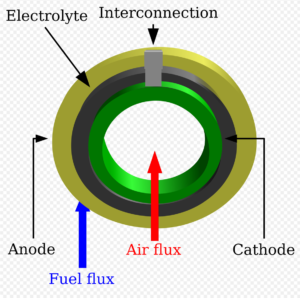
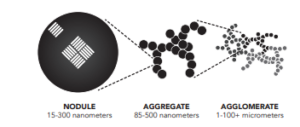
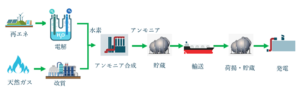
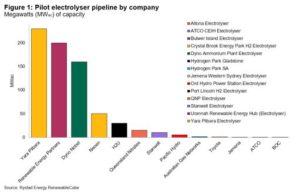
Most hydrogen today is produced from fossil fuels – steam methane reforming of natural gas, partial oxidation of coal or oil residues – and entails large CO2 emissions. This fossil hydrogen can be called “grey hydrogen”. Or sometimes, brown. The same color scheme applies to the ammonia produced from it, so we have “grey ammonia.” Or brown ammonia, your call. The exact carbon footprint depends on the fuel used and the efficiency of the facility, so you could easily identify many shades of grey.
There is, however, another option to deliver clean hydrogen – and now another colour: turquoise, or green-blue (or blue-green). This is the colour of hydrogen from methane pyrolysis, a process that directly splits methane into hydrogen and solid carbon. Instead of being a waste, like CO2, that must be disposed of safely, solid carbon is potentially a resource.