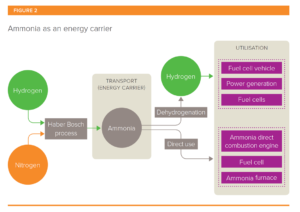
Ammonia for Power: a literature review
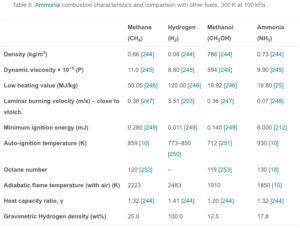
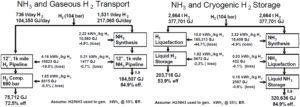
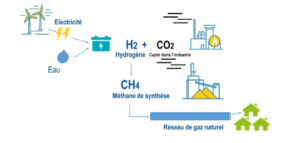
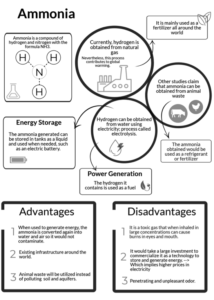
"Ammonia for Power" is an open-access literature review that includes over 300 citations for recent and ongoing research in the use of ammonia in engines, fuel cells, and turbines, as well as providing references to decades of historical case studies and publications. The review, written by a consortium of ammonia energy experts from the University of Cardiff, University of Oxford, the UK's Science and Technology Facilities Council, and Tsinghua University in China, can be found in the November 2018 edition of Progress in Energy and Combustion Science.