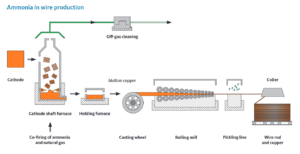
Aurubis to test using ammonia fuel for copper wire production in Germany
A shipment of thirteen tonnes of CCS-based ammonia has arrived in Hamburg from ADNOC’s al Ruwais ammonia plant near Abu Dhabi. This “demonstration cargo” has been in the works since March this year, when ADNOC signed an agreement with a raft of German organisations, including metals manufacturing giant Aurubis. The ammonia will be trialed as fuel to power copper rod production at Aurubis’ Hamburg smelter.