Ammonigy: Speedboats powered by green ammonia
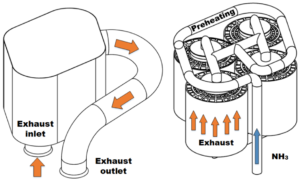
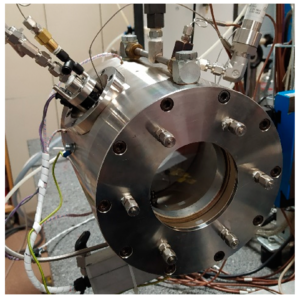
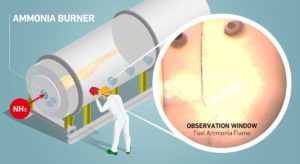
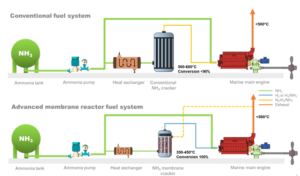
In order to demonstrated ammonia-fueled solutions in a variety of applications, Stuttgart-based organisation Ammonigy has developed two patented technologies: a modular cracking unit that provides hydrogen to act as an “igniter” for the ammonia fuel, and an exhaust treatment system to minimise NOx emissions from the engine. But, while the principles behind Ammonigy’s technology solutions are very familiar to our readers, using them to convert a speedboat to run on ammonia fuel is certainly new! This week we explore results from testing on the GREEN AMY: the world’s first ammonia-powered speedboat.